Tsukuba Machining Factory
The Fourth Machining Factory, located at the foothills of Mount Tsukuba in Ibaraki Prefecture, started operation in September 2018. Robot components such as those for ARC Mate and R-2000 are machined here. The Factory area is approximately 40,000 square meters and is the largest among FANUC’s machining factories. Everything is automated “from input to output,” by connecting each process, consisting of receiving, machining, finishing and inspecting, with AGVs. Furthermore, a conveyor links the Machining Factory to the Robot Factory next to it, smoothly supplying machined components to be assembled.
In the receiving process, the setting of workpieces, which are the raw materials, is automated by making full use of bin picking technology. An electromagnet or a vacuum hand is used depending on the workpiece material, to pick up workpieces arranged randomly. As the shape of robot components are complex, attachable/detachable robot hands with different types of finger tips can be switched to suit the workpiece. In this fashion, the scale of automation continues to expand.
In the machining process, 13 systems of FANUC robot cells, each consisting of four to six machining machines and four to six robots, have been installed, for long hours of continuous unmanned operation. In these cells, robots detect the position of the workpiece with a vision sensor, then grips the workpiece with a servo hand, adjusting to the workpiece’s size, to automate the loading and unloading of the workpiece on the machining jig. Consequently, preventing minor stoppages becomes key to factory operation. In this factory, when a problem occurs, such as when a vision sensor fails to detect, the process is repeated without any stops in a systematic manner, thus enabling stable operation for a long duration.
After the machining process, deburring and cleaning is performed in the finishing process. In this process, a system has been set up with which a large robot holds a workpiece while a small robot deburrs it. By gripping the workpiece and changing its orientation freely, the task of attaching workpieces to jigs, which was performed by humans up to now, can be omitted, expanding the application range of deburring by robots.
In the inspection process, the supply of workpieces to a coordinate measuring machine is automated. Moreover, processes which are difficult to automate, such as visual inspection and screw inspection, are ongoing challenges that continue to be actively tackled.
The factory is equipped with FANUC’s FIELD system Basic Package as an IoT platform. With this, the operating state of manufacturing equipment and the progress of machining are monitored. Also, an environmental sensor is connected to monitor and control the temperature and humidity within the factory. With this, a work-friendly environment (effective for preventing heatstroke) is maintained, and excessive consumption of energy can be avoided.
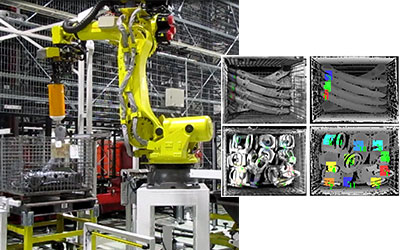
Bin picking of material

AGV

Robotized deburring system applying
the gripping method
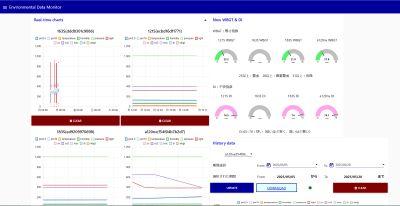
Factory temperature and humidity data